 1.Let your PC boot up completely before opening any applications.2.Refresh the desktop after closing any application. This will remove any unused files from the RAM.3.Do not set very large file size images as your wallpaper. Do not keep a wallpaper at all if your PC is low on RAM (less than 64 MB).4.Do not clutter your Desktop with a lot of shortcuts. Each shortcut on the desktop uses up to 500 bytes of RAM5.Empty the recycle bin regularly. The files are not really deleted from your hard drive until you empty the recycle bin.6.Delete the temporary internet files regularly.7.Defragment your hard drive once every two months. This will free up a lot of space on your hard drive and rearrange the files so that your applications run faster.8.Always make two partitions in your hard drive. Install all large Softwares (like PSP, Photoshop, 3DS Max etc) in the second partition. Windows uses all the available empty space in C drive as virtual memory when your Computer RAM is full. Keep the C Drive as empty as possible.9.When installing new Softwares disable the option of having a tray icon. The tray icons use up available RAM, and also slow down the booting of your PC. Also disable the option of starting the application automatically when the PC boots. You can disable these options later on also from the Tools or preferences menu in your application.10. Protect your PC from dust. Dust causes the CPU cooling fan to jam and slow down thereby gradually heating your CPU and affecting the processing speed. Use compressed air to blow out any dust from the CPU. Never use vacuum.RAM IS THE WORKING AREA (DESKTOP) OF THE CPU, KEEP IT AS EMPTY AND UNCLUTTERED AS POSSIBLE!
1.Let your PC boot up completely before opening any applications.2.Refresh the desktop after closing any application. This will remove any unused files from the RAM.3.Do not set very large file size images as your wallpaper. Do not keep a wallpaper at all if your PC is low on RAM (less than 64 MB).4.Do not clutter your Desktop with a lot of shortcuts. Each shortcut on the desktop uses up to 500 bytes of RAM5.Empty the recycle bin regularly. The files are not really deleted from your hard drive until you empty the recycle bin.6.Delete the temporary internet files regularly.7.Defragment your hard drive once every two months. This will free up a lot of space on your hard drive and rearrange the files so that your applications run faster.8.Always make two partitions in your hard drive. Install all large Softwares (like PSP, Photoshop, 3DS Max etc) in the second partition. Windows uses all the available empty space in C drive as virtual memory when your Computer RAM is full. Keep the C Drive as empty as possible.9.When installing new Softwares disable the option of having a tray icon. The tray icons use up available RAM, and also slow down the booting of your PC. Also disable the option of starting the application automatically when the PC boots. You can disable these options later on also from the Tools or preferences menu in your application.10. Protect your PC from dust. Dust causes the CPU cooling fan to jam and slow down thereby gradually heating your CPU and affecting the processing speed. Use compressed air to blow out any dust from the CPU. Never use vacuum.RAM IS THE WORKING AREA (DESKTOP) OF THE CPU, KEEP IT AS EMPTY AND UNCLUTTERED AS POSSIBLE!
 Google is clearly the best general-purpose search engine on the Web.But most people don’t use it to its best advantage or in an advanced way. Do you just plug in a keyword or two and hope for the best? That may be the quickest way to search, but with more than 3 billion pages in Google’s index, it’s still a struggle to pare results to a manageable number. There are some ways in which advanced Google search can be used to get the desired results.But Google is an remarkably powerful tool that can ease and enhance your Internet exploration. Advanced Google search options go beyond simple keywords, the Web, and even its own programmers. Let’s look at some of the advanced Google search options.Syntax Search TricksUsing a special syntax is a way to tell Google that you want to restrict your searches to certain elements or characteristics of Web pages.Here are some advanced Google search operators that can help narrow down your search results.1.Intitle: at the beginning of a query word or phrase restricts your search results to just the titles of Web pages.2.Intext: does the opposite of intitle:, searching only the body text, ignoring titles, links, and so forth. Intext: is perfect when what you’re searching for might commonly appear in URLs. If you’re looking for the term HTML, for example, and you don’t want to get results such aswww.tipsz.blogspot.com/you can enter intext:html3.Link: lets you see which pages are linking to your Web page or to another page you’re interested in. For example, try typing in link:http://www.tipsz.blogspot.com/3.site: (which restricts results to top-level domains) with intitle: to find certain types of pages. For example, get scholarly pages about Mark Twain by searching for intitle:”Mark Twain”site:edu. Experiment with mixing various elements; you’ll develop several strategies for finding the stuff you want more effectively. The site: command is very helpful as an alternative to the mediocre search engines built into many sites.Swiss Army GoogleGoogle has a number of services that can help you accomplish tasks you may never have thought to use Google for. For example, the new calculator feature(www.google.com/help/features.html#calculator) lets you do both math and a variety of conversions from the search box. For extra fun, try the query “Answer to life the universe and everything.”Suppose you want to contact someone and don’t have his phone number handy. Google can help you with that, too. Just enter a name, city, and state. (The city is optional, but you must enter a state.) If a phone number matches the listing, you’ll see it at the top of the search results along with a map link to the address. If you’d rather restrict your results, use rphonebook: for residential listings or bphonebook: for business listings. If you’d rather use a search form for business phone listings, try Yellow Search(www.buzztoolbox.com/google/yellowsearch.shtml).Let Google help you figure out whether you’ve got the right spelling—and the right word—for your search. Enter a misspelled word or phrase into the query box (try “thre blund mise”) and Google may suggest a proper spelling. This doesn’t always succeed; it works best when the word you’re searching for can be found in a dictionary. Once you search for a properly spelled word, look at the results page, which repeats your query. (If you’re searching for “three blind mice,” underneath the search window will appear a statement such as Searched the web for “three blind mice.”) You’ll discover that you can click on each word in your search phrase and get a definition from a dictionary.Extended GooglingGoogle offers several advanced services that give you a head start in focusing your search. Google Groups (http://groups.google.com/)indexes literally millions of messages from decades of discussion on Usenet. Google even helps you with your shopping via two tools: FroogleCODE(http://froogle.google.com/),which indexes products from online stores, and Google CatalogsCODE(http://catalogs.google.com/),which features products from more 6,000 paper catalogs in a searchable index. And this only scratches the surface. You can get a complete list of Google’s tools and services atwww.google.com/options/index.htmlYou’re probably used to using Google in your browser. But have you ever thought of using Google outside your browser?Google Alert(http://www.googlealert.com/)monitors your search terms and e-mails you information about new additions to Google’s Web index. (Google Alert is not affiliated with Google; it uses Google’s Web services API to perform its searches.) If you’re more interested in news stories than general Web content, check out the beta version of Google News Alerts(www.google.com/newsalerts).This advanced Google service (which is affiliated with Google) will monitor up to 50 news queries per e-mail address and send you information about news stories that match your query. (Hint: Use the intitle: and source: syntax elements with Google News to limit the number of alerts you get.)Google on the telephone? Yup. This service is brought to you by the folks at Google Labs(http://labs.google.com/),a place for experimental Google ideas and features (which may come and go, so what’s there at this writing might not be there when you decide to check it out).With Google Voice Search(http://labs1.google.com/gvs.html),you dial the Voice Search phone number, speak your keywords, and then click on the indicated link. Every time you say a new search term, the results page will refresh with your new query (you must have JavaScript enabled for this to work). Remember, this service is still in an experimental phase, so don’t expect 100 percent success.In 2002, Google released the Google API (application programming interface), a way for programmers to access Google’s search engine results without violating the Google Terms of Service. A lot of people have created useful (and occasionally not-so-useful but interesting) applications not available from Google itself, such as Google Alert. For many applications, you’ll need an API key, which is available free fromCODE www.google.com/apis
Google is clearly the best general-purpose search engine on the Web.But most people don’t use it to its best advantage or in an advanced way. Do you just plug in a keyword or two and hope for the best? That may be the quickest way to search, but with more than 3 billion pages in Google’s index, it’s still a struggle to pare results to a manageable number. There are some ways in which advanced Google search can be used to get the desired results.But Google is an remarkably powerful tool that can ease and enhance your Internet exploration. Advanced Google search options go beyond simple keywords, the Web, and even its own programmers. Let’s look at some of the advanced Google search options.Syntax Search TricksUsing a special syntax is a way to tell Google that you want to restrict your searches to certain elements or characteristics of Web pages.Here are some advanced Google search operators that can help narrow down your search results.1.Intitle: at the beginning of a query word or phrase restricts your search results to just the titles of Web pages.2.Intext: does the opposite of intitle:, searching only the body text, ignoring titles, links, and so forth. Intext: is perfect when what you’re searching for might commonly appear in URLs. If you’re looking for the term HTML, for example, and you don’t want to get results such aswww.tipsz.blogspot.com/you can enter intext:html3.Link: lets you see which pages are linking to your Web page or to another page you’re interested in. For example, try typing in link:http://www.tipsz.blogspot.com/3.site: (which restricts results to top-level domains) with intitle: to find certain types of pages. For example, get scholarly pages about Mark Twain by searching for intitle:”Mark Twain”site:edu. Experiment with mixing various elements; you’ll develop several strategies for finding the stuff you want more effectively. The site: command is very helpful as an alternative to the mediocre search engines built into many sites.Swiss Army GoogleGoogle has a number of services that can help you accomplish tasks you may never have thought to use Google for. For example, the new calculator feature(www.google.com/help/features.html#calculator) lets you do both math and a variety of conversions from the search box. For extra fun, try the query “Answer to life the universe and everything.”Suppose you want to contact someone and don’t have his phone number handy. Google can help you with that, too. Just enter a name, city, and state. (The city is optional, but you must enter a state.) If a phone number matches the listing, you’ll see it at the top of the search results along with a map link to the address. If you’d rather restrict your results, use rphonebook: for residential listings or bphonebook: for business listings. If you’d rather use a search form for business phone listings, try Yellow Search(www.buzztoolbox.com/google/yellowsearch.shtml).Let Google help you figure out whether you’ve got the right spelling—and the right word—for your search. Enter a misspelled word or phrase into the query box (try “thre blund mise”) and Google may suggest a proper spelling. This doesn’t always succeed; it works best when the word you’re searching for can be found in a dictionary. Once you search for a properly spelled word, look at the results page, which repeats your query. (If you’re searching for “three blind mice,” underneath the search window will appear a statement such as Searched the web for “three blind mice.”) You’ll discover that you can click on each word in your search phrase and get a definition from a dictionary.Extended GooglingGoogle offers several advanced services that give you a head start in focusing your search. Google Groups (http://groups.google.com/)indexes literally millions of messages from decades of discussion on Usenet. Google even helps you with your shopping via two tools: FroogleCODE(http://froogle.google.com/),which indexes products from online stores, and Google CatalogsCODE(http://catalogs.google.com/),which features products from more 6,000 paper catalogs in a searchable index. And this only scratches the surface. You can get a complete list of Google’s tools and services atwww.google.com/options/index.htmlYou’re probably used to using Google in your browser. But have you ever thought of using Google outside your browser?Google Alert(http://www.googlealert.com/)monitors your search terms and e-mails you information about new additions to Google’s Web index. (Google Alert is not affiliated with Google; it uses Google’s Web services API to perform its searches.) If you’re more interested in news stories than general Web content, check out the beta version of Google News Alerts(www.google.com/newsalerts).This advanced Google service (which is affiliated with Google) will monitor up to 50 news queries per e-mail address and send you information about news stories that match your query. (Hint: Use the intitle: and source: syntax elements with Google News to limit the number of alerts you get.)Google on the telephone? Yup. This service is brought to you by the folks at Google Labs(http://labs.google.com/),a place for experimental Google ideas and features (which may come and go, so what’s there at this writing might not be there when you decide to check it out).With Google Voice Search(http://labs1.google.com/gvs.html),you dial the Voice Search phone number, speak your keywords, and then click on the indicated link. Every time you say a new search term, the results page will refresh with your new query (you must have JavaScript enabled for this to work). Remember, this service is still in an experimental phase, so don’t expect 100 percent success.In 2002, Google released the Google API (application programming interface), a way for programmers to access Google’s search engine results without violating the Google Terms of Service. A lot of people have created useful (and occasionally not-so-useful but interesting) applications not available from Google itself, such as Google Alert. For many applications, you’ll need an API key, which is available free fromCODE www.google.com/apis
 Did you know that by changing a few settings you can make your dial-up modem run better? That's right you might have a fast modem and a good connection, but you are not getting the best performance. With a few adjustments, you can get faster connection speeds.NOTE: Since every PC configuration is different, these adjustments might not work for everyone.With Windows 95, 98 & ME you'll need to open your Control Panel ( Start / Control Panel ). Click "System" then choose "Device Manager". Open up "Ports", highlight your modem port (should be COM2), and choose "Properties" near the bottom. When you click "Port Settings", you will see the modem speed listed under "Bits per second".With Win XP , just hold down the Alt key and double-click "My Computer" to bring up System Properties. Click the "Hardware" tab, then choose the "Device Manager" button. Scroll down to "Modems" and click the little (—) to show your modem, then double click it.Selecting the "Modem" tab will allow you to adjust the port speed.Usually, the Maximum Port Speed is on the highest setting (115,000 bps), but sometimes you will find it on a slower default of 9600 bps. If you have a 56k modem, you can crank it up to the maximum setting without any trouble (in most cases). If you live in a cave and have a 28k modem, then the fastest you can do is 57,600 bps.Win 9x users should also adjust the "Flow Control" near the bottom. The default for this is usually Xon/Xoff which is the software control—change this to "Hardware" if you want to get the most from your modem. Next, click the "Advanced" button to adjust the Receiver Buffer to its highest setting (all the way to the right). If you run into any problems, just turn this one back to the 2/3 setting.To check/adjust the Receive-Transmit buffers in XP, click the "Advanced" tab of your modem properties then choose the "Advanced Port Settings" button. Make sure that both are set to their highest settings.There are many more tweaks that can be done in the registry, but the potential for disaster is too high for the average user. Some folks install dial-up accelerators, which basically tweak these registry settings for you and perform other routines to optimize performance.Just by changing these few settings, though, you should see better performance.
Did you know that by changing a few settings you can make your dial-up modem run better? That's right you might have a fast modem and a good connection, but you are not getting the best performance. With a few adjustments, you can get faster connection speeds.NOTE: Since every PC configuration is different, these adjustments might not work for everyone.With Windows 95, 98 & ME you'll need to open your Control Panel ( Start / Control Panel ). Click "System" then choose "Device Manager". Open up "Ports", highlight your modem port (should be COM2), and choose "Properties" near the bottom. When you click "Port Settings", you will see the modem speed listed under "Bits per second".With Win XP , just hold down the Alt key and double-click "My Computer" to bring up System Properties. Click the "Hardware" tab, then choose the "Device Manager" button. Scroll down to "Modems" and click the little (—) to show your modem, then double click it.Selecting the "Modem" tab will allow you to adjust the port speed.Usually, the Maximum Port Speed is on the highest setting (115,000 bps), but sometimes you will find it on a slower default of 9600 bps. If you have a 56k modem, you can crank it up to the maximum setting without any trouble (in most cases). If you live in a cave and have a 28k modem, then the fastest you can do is 57,600 bps.Win 9x users should also adjust the "Flow Control" near the bottom. The default for this is usually Xon/Xoff which is the software control—change this to "Hardware" if you want to get the most from your modem. Next, click the "Advanced" button to adjust the Receiver Buffer to its highest setting (all the way to the right). If you run into any problems, just turn this one back to the 2/3 setting.To check/adjust the Receive-Transmit buffers in XP, click the "Advanced" tab of your modem properties then choose the "Advanced Port Settings" button. Make sure that both are set to their highest settings.There are many more tweaks that can be done in the registry, but the potential for disaster is too high for the average user. Some folks install dial-up accelerators, which basically tweak these registry settings for you and perform other routines to optimize performance.Just by changing these few settings, though, you should see better performance.
 Really easy. But this only works if the original motherboard and harddrive still work. so put it back together. for newbies.
Really easy. But this only works if the original motherboard and harddrive still work. so put it back together. for newbies.
go to control panel > double-click the system icon > hardware tab and click device manager button. find the IDE ATA/ATAPI CONTROLLERS and expand the tab. not the primary or secondary controller, but right-click the first controller. choose update driver. choose the option to install from a list or specific location. click next. now choose the (don't search. I will choose the driver to install) option. click next. now highlight the Standard Dual Channel Pci Ide Controller. click next. the Standard controller will install. now reboot. log in. the standard controller is completely installed. you can now shutdown the computer, remove your harddrive, and it will boot with the new motherboard. i've done this 24 times on 12 different computers. it works.
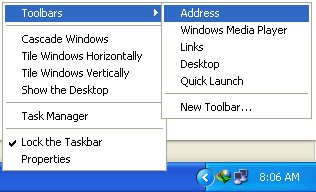 You can add an Internet URL address bar to your Windows XP taskbar. Doing so will let you type in URLs and launch Web pages without first launching a browser. It will also let you launch some native Windows XP applications in much the same way as you would via the Run menu (so you could type in calc to launch the calculator or mspaint to launch Microsoft Paint. Here's how you add the address bar:1. Right-click on the taskbar, select Toolbars, and then click Address.2. The word Address will appear on your taskbar.3. Double click it to access it.4. If that doesn't work, your taskbar is locked. You can unlock it by right-clicking on the taskbar again and uncheck Lock the Taskbar.NOTE: You may also need to grab the vertical dotted lines beside the word Address and drag it to the left to make the Address window appear.
You can add an Internet URL address bar to your Windows XP taskbar. Doing so will let you type in URLs and launch Web pages without first launching a browser. It will also let you launch some native Windows XP applications in much the same way as you would via the Run menu (so you could type in calc to launch the calculator or mspaint to launch Microsoft Paint. Here's how you add the address bar:1. Right-click on the taskbar, select Toolbars, and then click Address.2. The word Address will appear on your taskbar.3. Double click it to access it.4. If that doesn't work, your taskbar is locked. You can unlock it by right-clicking on the taskbar again and uncheck Lock the Taskbar.NOTE: You may also need to grab the vertical dotted lines beside the word Address and drag it to the left to make the Address window appear.
 General Keyboard ShortcutsCTRL+C (Copy)CTRL+X (Cut)CTRL+V (Paste)CTRL+Z (Undo)DELETE (Delete)SHIFT+DELETE (Delete the selected item permanently without placing the item in the Recycle Bin)CTRL while dragging an item (Copy the selected item)CTRL+SHIFT while dragging an item (Create a shortcut to the selected item)F2 key (Rename the selected item)CTRL+RIGHT ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the next word)CTRL+LEFT ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous word)CTRL+DOWN ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the next paragraph)CTRL+UP ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous paragraph)CTRL+SHIFT with any of the arrow keys (Highlight a block of text)SHIFT with any of the arrow keys (Select more than one item in a window or on the desktop, or select text in a document)CTRL+A (Select all)F3 key (Search for a file or a folder)ALT+ENTER (View the properties for the selected item)ALT+F4 (Close the active item, or quit the active program)ALT+ENTER (Display the properties of the selected object)ALT+SPACEBAR (Open the shortcut menu for the active window)CTRL+F4 (Close the active document in programs that enable you to have multiple documents open simultaneously)ALT+TAB (Switch between the open items)ALT+ESC (Cycle through items in the order that they had been opened)F6 key (Cycle through the screen elements in a window or on the desktop)F4 key (Display the Address bar list in My Computer or Windows Explorer)SHIFT+F10 (Display the shortcut menu for the selected item)ALT+SPACEBAR (Display the System menu for the active window)CTRL+ESC (Display the Start menu)ALT+Underlined letter in a menu name (Display the corresponding menu)Underlined letter in a command name on an open menu (Perform the corresponding command)F10 key (Activate the menu bar in the active program)RIGHT ARROW (Open the next menu to the right, or open a submenu)LEFT ARROW (Open the next menu to the left, or close a submenu)F5 key (Update the active window)BACKSPACE (View the folder one level up in My Computer or Windows Explorer)ESC (Cancel the current task)SHIFT when you insert a CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive (Prevent the CD-ROM from automatically playing)Dialog Box Keyboard ShortcutsCTRL+TAB (Move forward through the tabs)CTRL+SHIFT+TAB (Move backward through the tabs)TAB (Move forward through the options)SHIFT+TAB (Move backward through the options)ALT+Underlined letter (Perform the corresponding command or select the corresponding option)ENTER (Perform the command for the active option or button)SPACEBAR (Select or clear the check box if the active option is a check box)Arrow keys (Select a button if the active option is a group of option buttons)F1 key (Display Help)F4 key (Display the items in the active list)BACKSPACE (Open a folder one level up if a folder is selected in the Save As or Open dialog box)Microsoft Natural Keyboard ShortcutsWindows Logo (Display or hide the Start menu)Windows Logo+BREAK (Display the System Properties dialog box)Windows Logo+D (Display the desktop)Windows Logo+M (Minimize all of the windows)Windows Logo+SHIFT+M (Restore the minimized windows)Windows Logo+E (Open My Computer)Windows Logo+F (Search for a file or a folder)CTRL+Windows Logo+F (Search for computers)Windows Logo+F1 (Display Windows Help)Windows Logo+ L (Lock the keyboard)Windows Logo+R (Open the Run dialog box)Windows Logo+U (Open Utility Manager)Accessibility Keyboard ShortcutsRight SHIFT for eight seconds (Switch FilterKeys either on or off)Left ALT+left SHIFT+PRINT SCREEN (Switch High Contrast either on or off)Left ALT+left SHIFT+NUM LOCK (Switch the MouseKeys either on or off)SHIFT five times (Switch the StickyKeys either on or off)NUM LOCK for five seconds (Switch the ToggleKeys either on or off)Windows Logo +U (Open Utility Manager)Windows Explorer Keyboard ShortcutsEND (Display the bottom of the active window)HOME (Display the top of the active window)NUM LOCK+Asterisk sign (*) (Display all of the subfolders that are under the selected folder)NUM LOCK+Plus sign (+) (Display the contents of the selected folder)NUM LOCK+Minus sign (-) (Collapse the selected folder)LEFT ARROW (Collapse the current selection if it is expanded, or select the parent folder)RIGHT ARROW (Display the current selection if it is collapsed, or select the first subfolder)Shortcut Keys for Character MapAfter you double-click a character on the grid of characters, you can move through the grid by
General Keyboard ShortcutsCTRL+C (Copy)CTRL+X (Cut)CTRL+V (Paste)CTRL+Z (Undo)DELETE (Delete)SHIFT+DELETE (Delete the selected item permanently without placing the item in the Recycle Bin)CTRL while dragging an item (Copy the selected item)CTRL+SHIFT while dragging an item (Create a shortcut to the selected item)F2 key (Rename the selected item)CTRL+RIGHT ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the next word)CTRL+LEFT ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous word)CTRL+DOWN ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the next paragraph)CTRL+UP ARROW (Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous paragraph)CTRL+SHIFT with any of the arrow keys (Highlight a block of text)SHIFT with any of the arrow keys (Select more than one item in a window or on the desktop, or select text in a document)CTRL+A (Select all)F3 key (Search for a file or a folder)ALT+ENTER (View the properties for the selected item)ALT+F4 (Close the active item, or quit the active program)ALT+ENTER (Display the properties of the selected object)ALT+SPACEBAR (Open the shortcut menu for the active window)CTRL+F4 (Close the active document in programs that enable you to have multiple documents open simultaneously)ALT+TAB (Switch between the open items)ALT+ESC (Cycle through items in the order that they had been opened)F6 key (Cycle through the screen elements in a window or on the desktop)F4 key (Display the Address bar list in My Computer or Windows Explorer)SHIFT+F10 (Display the shortcut menu for the selected item)ALT+SPACEBAR (Display the System menu for the active window)CTRL+ESC (Display the Start menu)ALT+Underlined letter in a menu name (Display the corresponding menu)Underlined letter in a command name on an open menu (Perform the corresponding command)F10 key (Activate the menu bar in the active program)RIGHT ARROW (Open the next menu to the right, or open a submenu)LEFT ARROW (Open the next menu to the left, or close a submenu)F5 key (Update the active window)BACKSPACE (View the folder one level up in My Computer or Windows Explorer)ESC (Cancel the current task)SHIFT when you insert a CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive (Prevent the CD-ROM from automatically playing)Dialog Box Keyboard ShortcutsCTRL+TAB (Move forward through the tabs)CTRL+SHIFT+TAB (Move backward through the tabs)TAB (Move forward through the options)SHIFT+TAB (Move backward through the options)ALT+Underlined letter (Perform the corresponding command or select the corresponding option)ENTER (Perform the command for the active option or button)SPACEBAR (Select or clear the check box if the active option is a check box)Arrow keys (Select a button if the active option is a group of option buttons)F1 key (Display Help)F4 key (Display the items in the active list)BACKSPACE (Open a folder one level up if a folder is selected in the Save As or Open dialog box)Microsoft Natural Keyboard ShortcutsWindows Logo (Display or hide the Start menu)Windows Logo+BREAK (Display the System Properties dialog box)Windows Logo+D (Display the desktop)Windows Logo+M (Minimize all of the windows)Windows Logo+SHIFT+M (Restore the minimized windows)Windows Logo+E (Open My Computer)Windows Logo+F (Search for a file or a folder)CTRL+Windows Logo+F (Search for computers)Windows Logo+F1 (Display Windows Help)Windows Logo+ L (Lock the keyboard)Windows Logo+R (Open the Run dialog box)Windows Logo+U (Open Utility Manager)Accessibility Keyboard ShortcutsRight SHIFT for eight seconds (Switch FilterKeys either on or off)Left ALT+left SHIFT+PRINT SCREEN (Switch High Contrast either on or off)Left ALT+left SHIFT+NUM LOCK (Switch the MouseKeys either on or off)SHIFT five times (Switch the StickyKeys either on or off)NUM LOCK for five seconds (Switch the ToggleKeys either on or off)Windows Logo +U (Open Utility Manager)Windows Explorer Keyboard ShortcutsEND (Display the bottom of the active window)HOME (Display the top of the active window)NUM LOCK+Asterisk sign (*) (Display all of the subfolders that are under the selected folder)NUM LOCK+Plus sign (+) (Display the contents of the selected folder)NUM LOCK+Minus sign (-) (Collapse the selected folder)LEFT ARROW (Collapse the current selection if it is expanded, or select the parent folder)RIGHT ARROW (Display the current selection if it is collapsed, or select the first subfolder)Shortcut Keys for Character MapAfter you double-click a character on the grid of characters, you can move through the grid by
using the keyboard shortcuts:RIGHT ARROW (Move to the right or to the beginning of the next line)LEFT ARROW (Move to the left or to the end of the previous line)UP ARROW (Move up one row)DOWN ARROW (Move down one row)PAGE UP (Move up one screen at a time)PAGE DOWN (Move down one screen at a time)HOME (Move to the beginning of the line)END (Move to the end of the line)CTRL+HOME (Move to the first character)CTRL+END (Move to the last character)SPACEBAR (Switch between Enlarged and Normal mode when a character is selected)Microsoft Management Console (MMC) Main Window Keyboard ShortcutsCTRL+O (Open a saved console)CTRL+N (Open a new console)CTRL+S (Save the open console)CTRL+M (Add or remove a console item)CTRL+W (Open a new window)F5 key (Update the content of all console windows)ALT+SPACEBAR (Display the MMC window menu)ALT+F4 (Close the console)ALT+A (Display the Action menu)ALT+V (Display the View menu)ALT+F (Display the File menu)ALT+O (Display the Favorites menu)MMC Console Window Keyboard ShortcutsCTRL+P (Print the current page or active pane)ALT+Minus sign (-) (Display the window menu for the active console window)SHIFT+F10 (Display the Action shortcut menu for the selected item)F1 key (Open the Help topic, if any, for the selected item)F5 key (Update the content of all console windows)CTRL+F10 (Maximize the active console window)CTRL+F5 (Restore the active console window)ALT+ENTER (Display the Properties dialog box, if any, for the selected item)F2 key (Rename the selected item)CTRL+F4 (Close the active console window. When a console has only one console window, this shortcut closes the console)Remote Desktop Connection NavigationCTRL+ALT+END (Open the Microsoft Windows NT Security dialog box)ALT+PAGE UP (Switch between programs from left to right)ALT+PAGE DOWN (Switch between programs from right to left)ALT+INSERT (Cycle through the programs in most recently used order)ALT+HOME (Display the Start menu)CTRL+ALT+BREAK (Switch the client computer between a window and a full screen)ALT+DELETE (Display the Windows menu)CTRL+ALT+Minus sign (-) (Place a snapshot of the active window in the client on the Terminal server clipboard and provide the same functionality as pressing PRINT SCREEN on a local computer.)CTRL+ALT+Plus sign (+) (Place a snapshot of the entire client window area on the Terminal server clipboard and provide the same functionality as pressing ALT+PRINT SCREEN on a local computer.)Microsoft Internet Explorer NavigationCTRL+B (Open the Organize Favorites dialog box)CTRL+E (Open the Search bar)CTRL+F (Start the Find utility)CTRL+H (Open the History bar)CTRL+I (Open the Favorites bar)CTRL+L (Open the Open dialog box)CTRL+N (Start another instance of the browser with the same Web address)CTRL+O (Open the Open dialog box, the same as CTRL+L)CTRL+P (Open the Print dialog box)CTRL+R (Update the current Web page)CTRL+W (Close the current window)
 Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the latest version of photoshop.Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the industry-standard image editing software, used worldwide by professional photographers and designers who want to perfect their digital images, but due to its high price a very few number of people can afford itPreviously I wrote an article on Adobe Photoshop CS5 keygen, however some of readers had problems and faced difficulties in downloading them so in this article I will be posting Adobe CS5 Serial Numbers.Here are a Few working Adobe Photoshop CS5 Serial Numbers 1188-1702-9219-4234-2059-4581 1330-1281-8916-6015-7348-5124 1325-1558-5864-4422-1094-1126 1325-0621-9125-0765-3648-0614 1325-0365-5929-6118-8817-8422 1325-0150-1163-7532-1626-3430 1325-0178-1927-9019-0123-2254 1325-0702-3693-1544-9166-3515 1325-0549-2240-0071-3409-1342You Can also Download Adobe CS5 100% working Keygen if the above codes do not work for you
Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the latest version of photoshop.Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the industry-standard image editing software, used worldwide by professional photographers and designers who want to perfect their digital images, but due to its high price a very few number of people can afford itPreviously I wrote an article on Adobe Photoshop CS5 keygen, however some of readers had problems and faced difficulties in downloading them so in this article I will be posting Adobe CS5 Serial Numbers.Here are a Few working Adobe Photoshop CS5 Serial Numbers 1188-1702-9219-4234-2059-4581 1330-1281-8916-6015-7348-5124 1325-1558-5864-4422-1094-1126 1325-0621-9125-0765-3648-0614 1325-0365-5929-6118-8817-8422 1325-0150-1163-7532-1626-3430 1325-0178-1927-9019-0123-2254 1325-0702-3693-1544-9166-3515 1325-0549-2240-0071-3409-1342You Can also Download Adobe CS5 100% working Keygen if the above codes do not work for you
 1.Let your PC boot up completely before opening any applications.
1.Let your PC boot up completely before opening any applications.




